What is perfume? It is a mixture of fragrant essential
oils and/or aroma compounds, used to give a pleasant scent. We encounter perfumes, flavors and fragrances in many products we come into contact with each and every day
such as shampoos, cleaning products and personal fragrances. However, what are
often considered by the public to be ‘perfumes’ are in fact complex mixtures of
organic molecules, which may come from natural sources or synthetic routes.
Until the middle of 19th century, perfumes
were served for the wealthiest strata of society. But, now, everybody can
afford it. This dramatic change is because of the development of synthetic
organic chemistry. Aroma compounds can be found in food, wine, spices,
perfumes, fragrance oils, and essential oils. For example, many form
biochemically during ripening of fruits and other crops.
During ancient Egypt, the use of perfumes were very popular. They used fragrant materials in many forms such as pressed, boiled, dried, powdered, macerated in fat, or distillation. Many perfumes had more than a dozen ingredients. Nevertheless, the perfumes are also bottled in beautiful glasses. Aroma compounds can be classified by structure such as esters, linear terpenes, cyclic terpenes ,aromatics and amines. Other aroma compounds includes Alcohols, Aldehydes, Esters, Ketones, Lactones, Thiols.
Aldehydes are organic compounds present in many natural
materials (including roses), that also can be synthesized artificially. Aldehydes are organic compounds which have a carbonyl functional group (C=O). The carbon atom of this group
has two remaining bonds that may be occupied by hydrogen or alkyl or aryl
substituents.
The most widely used aldehydes in perfumery are:
C7
(possessing a herbaceous green aroma)
C8 (orange-like)
C9 (smelling of
roses)
C10 (evoking orange rind),
Citral, a complex 10-carbon aldehyde
(fragrance of lemons),
C11 (a clean, leafy green aroma)
C12 (the odor of
lilacs or violets)
C13 (waxy, with grapefruit undertone), and
C14 (evoking the
scent of peach-skin).
For an instance,
rose is currently an important scent in the class of floral fragrances.
IUPAC name :Tetrahydro-4-methyl-2-(2-methylpropenyl)-2H-pyran
The molecular formula is : C10H18O
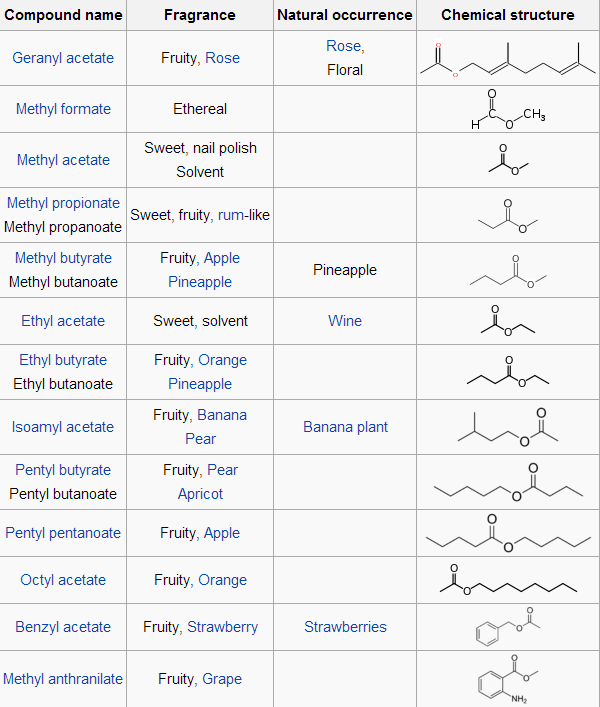
The table below is the examples of esters:
Perfume making process :
Collection
The first step in the perfume making process is collection of raw materials. Fragrance can be obtained from flowers, grasses,
mosses, leaves, tree barks and fruit peels.
Distillation
Raw materials are steamed. the scent is carried into a glass tube as the steam rises, where the mixture
condenses as it cools. The mixture is put into flask where the essential oil
naturally rises to the top and is skimmed off for use in the perfume.
Absorption
Absorption is used for raw materials that can't with
stand the heat of the distillation process. They are steeped in heated fats or
oils, then filtered through fabric to obtain the scented solid. The solid is
then washed in alcohol. The perfumed alcohol remains when the fat is removed.
Extraction
Fragrance also is drawn when plant matter and volatile
solvents are combined in a rotating tank. The solvent extracts the essential
oils and dissolves the plant matter, leaving a wax-like oil. Once the oil has
evaporated, a perfume paste remains.
Aromas
Musk and castor are animal secretions that were frequently used in
perfume making. Synthetically produced aromas also are used.
Blending
Once the perfume oil is extracted, the blending process takes place. A perfumer, known as "a nose," uses an extensive knowledge
of fragrance characteristic to blend anywhere from 20 to 800 raw materials to
compose a scent. Once the scent is developed and tested, batches are
robotically mixed.
The pure perfume oil is diluted with alcohol and
water.10 to 20 percent of the oil is dissolved
in alcohol with a minute amount of water if a full perfume is desired. Cologne is 3 to 5 percent oil, 80 to
90 percent alcohol and 10 percent water. An eau de toilette is 2 percent oil,
60 to 80 percent alcohol and 20 percent water. Then the perfume is ready to be
aged, filtered and bottled.
Circle of types of aromas and tastes :
Fragrances Pyramid :
Top notes(Head notes):
- The scents that are perceived immediately on
application of a perfume.
- consist of small, light molecules that evaporate
quickly.
- They form a person's initial impression of a perfume
and thus are very important in the selling of a perfume.
Middle notes(Heart notes):
-Scent are prior to the dissipation of the top note.
-The middle note compounds form the "heart" or
main body of a perfume and act to mask the often unpleasant initial impression
of base notes, which become more pleasant with time.
Base notes:
- Scent close to the departure of the middle notes.
-The base and middle notes together are the main theme of
a perfume. Base notes bring depth and solidity to a perfume.
-Usually not perceived until 30 minutes after
application.
Table of Aroma compounds and its quality:
Some beer contains aroma too, here are some of the examples:
Fragrance chemistry is an industrially important science that requires the constant
discovery of new and unique odorants.
References :
1. What are Aldehydes? <http://beauty.about.com/od/fragranc1/a/What-are-Aldehydes.htm> Accesed on 23 July 2014.
2. Jim Clark 2004.<http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/esters/background.html> Accessed on 23 July 2014.
3. Dr Anne Haron ,2010.< http://www.rsc.org/Membership/Networking/InterestGroups/OrganicDivision/organic-chemistry-case-studies/organic-chemistry-flavours.asp> Accessed on 23 July 2014.







.png)










.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

